Présentation du LIBAN
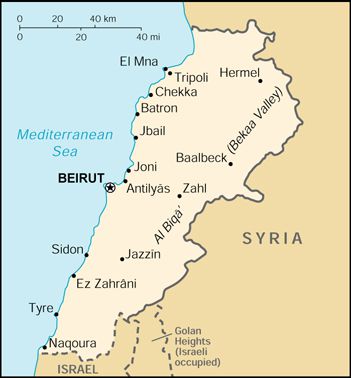
La Républiquelibanaise est un État du Proche-Orient (Asie de l'Ouest), en grande partie montagneux. Il partage ses frontières avec deux États, la Syrie au nord et à l'est, et Israël au sud. Il est bordé à l'ouest par le bassin Levantin, la partie orientale de la mer Méditerranée.
La capitale est Beyrouth et la langue officielle est l'arabe.
La monnaie nationale est la livre libanaise.
Du fait de sa composition pluriconfessionnelle, le Liban est doté d'un système politique fondé sur une répartition du pouvoir plus ou moins proportionnelle au poids de chaque communauté religieuse, c'est le confessionnalisme.
L'État libanais est créé sous le nom de Grand Liban en 1920 par la France par division du territoire ottoman dit de la « Grande Syrie », sur la base de l'entité autonome du 'Mont-Liban' complétée principalement par Beyrouth et la plaine dela Bekaa.
La Franceavait été alors, à la suite du démantèlement de l'empire ottoman, mandatée parla Sociétédes Nations pour développer et moderniser certains territoires ex-ottomans.
En 1926, le pays adopte sa première constitution, devient officiellement une République, prend le nom de République libanaise et crée les postes de Président dela République et de Président du Conseil des ministres.
Le drapeau du Liban est composé de trois bandes horizontales, deux rouges (en haut et en bas), représentant le sacrifice pour l'indépendance, et une blanche faisant le double d'une bande rouge représentant la neige qui couvre ses montagnes, la pureté et la paix. Le tout frappé en son centre par un cèdre vert, symbole par excellence du pays.
L’emblème du pays, est le cèdre du Liban, (Cedrus libani Pinacées). Son bois, imputrescible et très léger, aurait servi entre autres à la construction du Temple de Salomon à Jérusalem. Les Phéniciens s'en servaient également pour la construction de leurs légendaires navires. Ce drapeau tel qu'il est date de 1943.
Son Histoire, son système politique et la variété de sa culture, de sa démographie religieuse et de sa géographie en font un pays à part et original de l'Orient arabe. Le Liban a été occupé au cours des siècles par diverses civilisations. Il est aussi réputé dans le monde pour sa gastronomie et, dans le monde arabe, pour sa musique.
Le pays était considéré comme le coffre fort du Levant, et était connu comme « La Suisse du Moyen-Orient », du fait de son poids et de sa puissance financière. Le Liban a attiré de nombreux touristes, en grande partie parce que Beyrouth, la capitale, était connue comme le « Paris du Moyen-Orient ». Beyrouth a d'ailleurs été classée par le New York Times comme la première ville à visiter pour l'année 2009.
TheLebaneseRepublicis a state in the Middle East (West Asia), largely mountainous. It shares borders with two states,Syriato the north and east andIsraelto the south. It is bordered to the west by the Levantine basin, the easternMediterranean Sea.
The capital is Beirutand the official language is Arabic.
The national currency is the Lebanese pound.
Because of its multi-faith composition, Lebanon has a political system based on a distribution of power more or less proportional to the weight of each religious community is sectarianism.
The Lebanese state is created under the name of Greater Lebanon in 1920 by France, by division of Ottoman territory called "Greater Syria", on the basis of the autonomous entity of the "Mount Lebanon" Beirut and completed primarily by the Bekaa.
France was then, following the dismantling of the Ottoman Empire, mandated by the League of Nations to develop and modernize some former Ottoman territories.
In 1926 the country adopted its first constitution, officially became a Republic, takes the name of Republic of Lebanon and created the positions of President of the Republic and President of the Council of Ministers.
The flag of Lebanon is composed of three horizontal stripes, two red (top and bottom), representing the sacrifice for independence and making the double white with a red stripe represents the snow covered mountains, purity and peace. All struck in the middle by a green cedar tree, symbol of the country.
The emblem of the country is the cedar of Lebanon (Cedrus libani Pinaceae). Its wood, rot-proof and very light, have served include the construction of Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem. The Phoenicians used it also for the construction of their legendary ship.This flag as date of 1943.
Its history, its political system and the variety of its culture, its religious demographics and geography make it a separate country and original of the Arab East. Lebanon has been occupied for centuries by various civilizations. He is also renowned worldwide for its cuisine and in the Arab world for his music.
The country was considered the safe of the Levant, and was known as "Switzerland of the Middle East" because of its weight and its financial strength. Lebanon has attracted many tourists, largely because the capital, Beirut was known as the "Paris of the Middle East." Beirut has also been classified by the New York Times as the first city to visit in 2009.
La Repúblicadel Líbano es un estado en el Medio Oriente (Asia Occidental), en gran parte montañosa. Comparte fronteras con dos estados, Siria al norte y al este y al sur de Israel. Limita al oeste con la cuenca levantina, el este del mar Mediterráneo.
La capital es Beirut, y el idioma oficial es el árabe.
La moneda nacional es la libra libanesa.
Debido a su composición multi-religiosa, el Líbano tiene un sistema político basado en una distribución de poder más o menos proporcional al peso de cada comunidad religiosa es el sectarismo.
El Estado libanés se crea bajo el nombre de Gran Líbano en 1920 por Francia, por la división del territorio otomano llamado "Gran Siria", sobre la base de la entidad autónoma del "Monte Líbano" Beirut y completa sobre todo por el Bekaa.
Francia fue entonces, tras el desmantelamiento del Imperio Otomano, el mandato de la Liga de las Naciones Unidas para desarrollar y modernizar algunos antiguos territorios otomanos.
En 1926 el país adoptó su primera Constitución, se convirtió oficialmente en una República, toma el nombre de República del Líbano y creó el cargo de Presidente de la República y Presidente del Consejo de Ministros.
La bandera de Líbano, se compone de tres franjas horizontales, dos de color rojo (superior e inferior), lo que representa el sacrificio por la independencia y hacer el doble de blanco con una franja roja representa las montañas cubiertas de nieve, la pureza y la paz. Todos los golpeó en medio de un árbol de cedro verde, símbolo por excelencia del país.
El emblema del país, es el cedro del Líbano (Cedrus libani Pinaceae). Su madera, imputrescible y muy ligero, han servido incluyen la construcción del Templo de Salomón en Jerusalén. Los fenicios se utilizan también para la construcción de sus legendarios barcos. Esta bandera como la fecha de 1943.
Su historia, su sistema político y la variedad de su cultura, su demografía y la geografía religiosa que sea un país independiente y original del Oriente árabe. El Líbano ha sido ocupado durante siglos por diversas civilizaciones. También es reconocido mundialmente por su cocina y en el mundo árabe por su música.
El país era considerado la caja fuerte del Levante, y fue conocido como "la Suiza de Oriente Medio", debido a su peso y su solidez financiera. El Líbano ha atraído a muchos turistas, sobre todo porque la capital, Beirut era conocida como la "París del Medio Oriente". Beirut también ha sido clasificado por el New York Times como la primera ciudad a visitar en 2009.
Inscrivez-vous au blog
Soyez prévenu par email des prochaines mises à jour
Rejoignez les 2 autres membres